About Compression Ratio of Ring Die
Generally, a ring die corresponds to one compression ratio. It’s fixed, cannot be changed.
If the compression ratio is incorrect, then the reliable quality of biomass pellets cannot be guaranteed. This will bring irreparable losses. So it’s very important to know about the compression ratio of ring die.
The ring die compression ratio refers to the ratio of the effective working length of the ring die to the die hole diameter. Simply put, it is a matter of the length of time the raw material stays in the die. It also presents compress degree of biomass.
Calculation method of ring die compression ratio:
ring die compression ratio = die hole diameter / effective working length of die hole.For a ring die with straight holes, the effective length of the die hole is the total thickness of the die. Assuming: the diameter of the die hole is 6mm, the thickness of the ring die is 45mm , 6/45=1:7.5, then the compression ratio of this ring die is 1:7.5;
For a ring die with released stepped hole or released outer tapered hole, the effective length of the die hole is the total thickness of the die minus the length of the release hole, and the aperture of the smallest diameter section is the aperture for calculating the compression ratio. Assuming: the diameter of the ring die hole is 8mm, the die thickness is 66mm, and the depth of the release hole is 18mm. Compression ratio=8/(66-18)=1:6, the compression ratio of this ring die is 1:6.
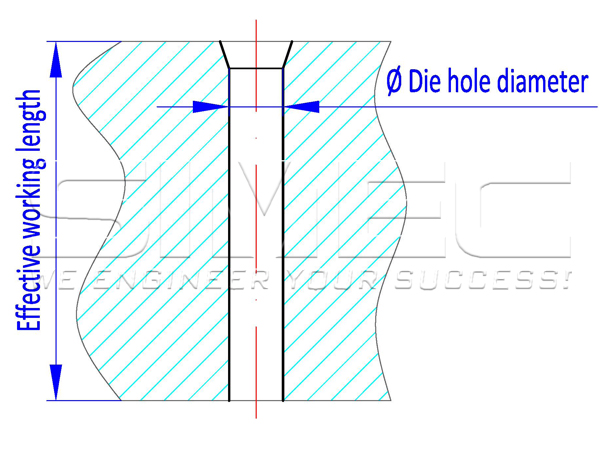
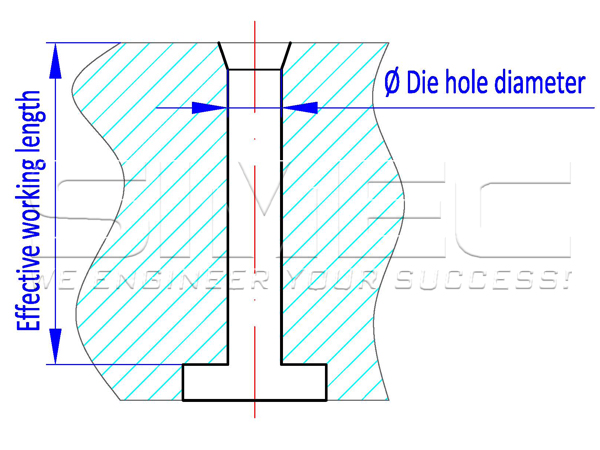
A low compression ratio can increase output, reduce energy consumption, and reduce wear of ring die and rollers, but if it's incorrectly designed, the biomass pellets may be loose, varying in length, and powder ratio may be high;
With high compression ratio, biomass pellets will be very solid, with smooth and shiny appearance, and low powdering rate. But if the ratio design is incorrect, the production cost will be very high.
The effect of compression ratio on pellet quality
SIMEC R&D team has researched the effect of ring die compression ratio on energy consumption and pellet quality. Let’s take a look at the specific results of analysis:
1. Impact on energy consumption
The compression ratio of ring die is significantly positively correlated with feeding amount of pellet machine (P<0.05); as the compression ratio increases, the pelletizing efficiency gradually increases.
Comparing the impact of different ring die compression ratios (1:5, 1:6) on pelletization, installing a ring die with a compression ratio of 1:6 will increase the pelletizing efficiency of pellet machine, reducing consumption by about 0.1% and reducing production costs, improving production quality and benefit.
2. Impact on pellet hardness
The effect of different compression ratios on pellet hardness: when ring die made of the same material, with the same aperture, produces pellets with the same cross-sectional shape, the pellet hardness will increase significantly with the increase of compression ratio.
3. Impact on powder ratio of biomass pellets
The powder radio of biomass pellets should be controlled within 5%. The results show that low compression ratio can reduce energy consumption, but pellet quality may decrease, such as loose and cracked, or high powder ratio; while the compression ratio is high, the quality of pellets will be correspondingly improved, and the appearance will be smooth without cracks. The powder ratio will be reduced.
4. The impact of compression ratio on raw material moisture control
The moisture content of raw material refers to the percentage of moisture contained in the raw material per unit mass. It is an important parameter that needs to be controlled during the pellet forming process.
If moisture content of raw material is too high or too low, it will directly affect the pellet forming speed. Different raw materials correspond different moisture content ranges for efficient pelletization. Like the ring die compression ratio, each raw material has an optimal moisture content to maximize its pelleting speed.
In order to accurately study the impact of the two parameters of moisture content and
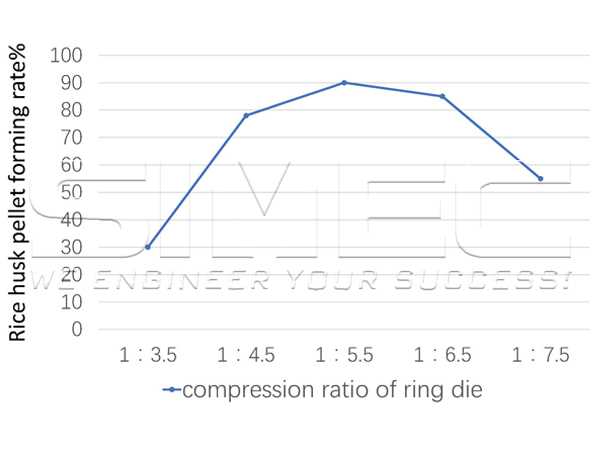
compression ratio on pellet forming rate, let's take a look at the analysis data of rice husk pelleting experiment:
As ring die compression ratio increases, the pellet forming ratio gradually increases, and when the compression ratio reaches 1:5.5, a peak occurs. Then, as ring die compression ratio increases, the pellet forming ratio gradually decreases.
This shows that the greater the compression ratio, the greater the forming pressure of pellets and the tighter pressure between the raw materials, which effectively improves the pelleting rate of rice husk.
However, if compression ratio of ring die is too high, then the forming pressure of pellets will be too high, and they will be tightly combined before being extruded from the die hole, resulting in an increase in the resistance between the pellets and the die holes, causing part of the die holes to be blocked, and the forming rate decreases.
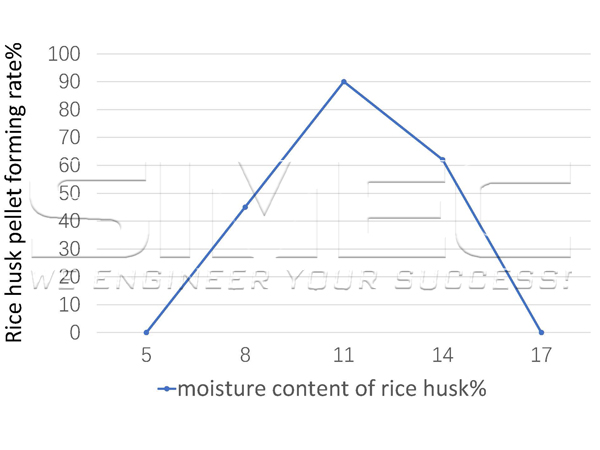
When moisture content of rice husk is 5%, pellet forming rate is 0, and when the moisture content reaches 8%, qualified pellets begin to be produced, and then as moisture content of rice husk increases, pellet forming rate is greatly improved;
When moisture content of rice husk reaches 11%, it reaches the peak value, but then as the moisture content increases, conversely the pellet forming rate decreases;
When moisture content of rice husk reaches 17%, the forming rate of pellets drops to 0;
When moisture content of rice husk is 8% and 14%, although pellet can be formed, the forming ratio is low.
This shows that moisture content has a great influence on pellet forming ratio. Proper moisture content is helpful for the forming of rice husk pellets, but if moisture content is too high, the moisture will form tension between the raw materials, expand the gap between the raw materials, and reduce the intermolecular interaction force, so that the pellet forming ratio is greatly reduced.
How to adjust between compression ratio and moisture content?
If the material moisture meets the requirements, but the pellets are soft and have a large expansion coefficient, the compression ratio of ring die needs to be increased; if the pellets are hard and even carbonized, the compression ratio needs to be appropriately reduced.
In the case of fixed compression ratio, the pellets are soft and have a large expansion coefficient, then the moisture of raw materials needs to be reduced (drying or adding materials with lower moisture); if the pellets are hard and even carbonized, then the moisture needs to be increased.
Generally, the compression ratio of ring die is custom-designed based on the analysis of raw material and specification requirements of pellets. Different types of pellet mills have different mechanical parameters, which also have a great impact on the design of compression ratio. Therefore, the selection method of compression ratio is not fixed, professional design is the most important.
© Copyright of articles and pictures on this site belongs to SIMEC. Any company, media, website or individual are not allowed to reprint, reproduce, repost, modify or use in other ways without permission. Otherwise SIMEC will have the right to pursue legal responsibilities.